Table Of Content
Serial blood samples (50–100 µL) were collected at 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8, 24 h after dosing and centrifuged at 7227 × g for 5 min to obtain the plasma fraction. A 10 μL aliquot of plasma was deproteinized with 100 μL acetonitrile/methanol (1/1, v/v) containing internal standard. After centrifugation, the supernatant was diluted with a certain proportion of acetonitrile/water (1/1, v/v), mixed and centrifuged at 1807 × g for 10 min. Finally, the aliquots of the diluted supernatant were injected into LC–MS/MS system. 293T cells transfected with Flag-RNF130 for 48 h were collected and lysed in 20 mM Tris pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl and 1% Triton X-100.
Mass spectrometry analysis
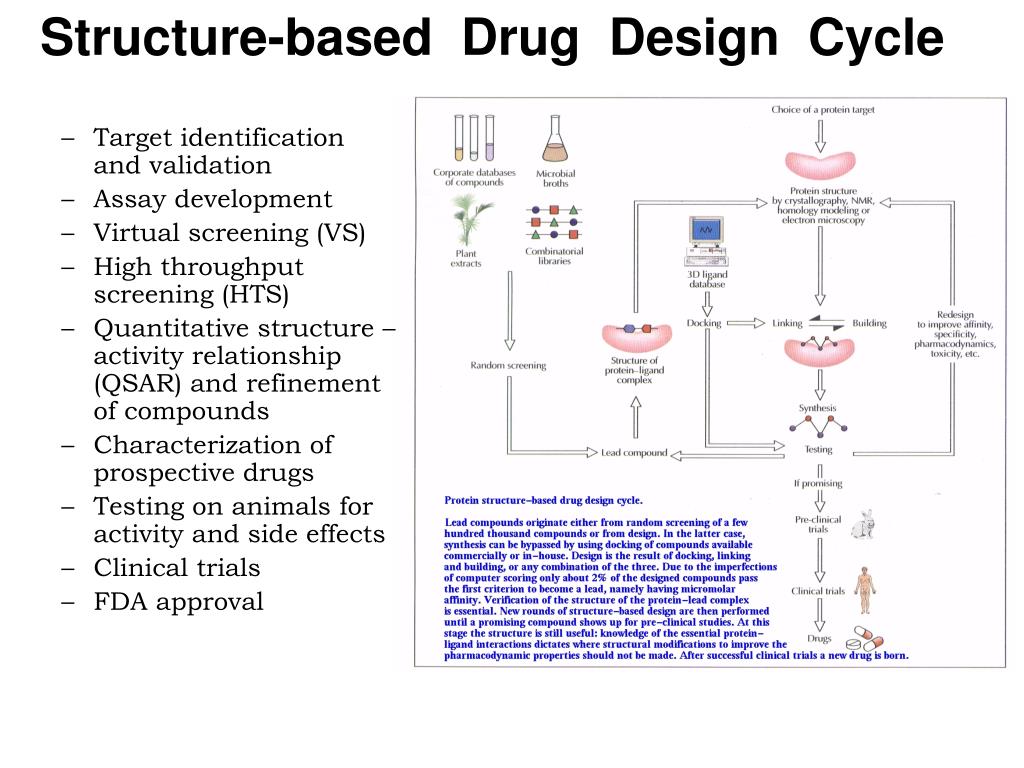
Rational Approaches to Lead Discovery None of the above approaches to lead discovery involves a major rational component. The lead is just found by screening techniques, as a by-product of drug metabolism studies, or from clinical investigations. Rational approaches to drug design now have become the major routes to lead discovery.
Current Methods for Drug Design
Although such details were not present in the ChEMBL database, recognizing these distinct binding sites was deemed essential for effective drug-target interactome learning.molecules known for their allosteric modulation were extracted from the reference cited as Ref. 95. Subsequently, the drug-target graph underwent a modification whereby target-IDs encompassing both allosteric and orthosteric ligands were treated as distinct target-IDs. The replacement of methyl (Me or −CH3) with trifluoromethyl (TFM or −CF3) is frequently employed in compound optimization. However, the exact effect of −CH3/–CF3 substitution on bioactivity is still controversial. To further investigate whether TransformerCPI2.0 captures the key features of the compound and comprehensively understands compound–protein interaction, we employed TransformerCPI2.0 to predict the substitution effect of the trifluoromethyl group. We utilized a previously reported dataset, removed the redundancy data and finally got a dataset containing 18,217 pairs of compounds and corresponding bioactivity data with the only difference being that −CH3 is substituted by −CF3 to study this problem.
Pharmaceutical and Health Economics Graduate Programs
Obtaining a good quality QSAR model depends on many factors, such as the quality of input data, the choice of descriptors and statistical methods for modeling and for validation. Any QSAR modeling should ultimately lead to statistically robust and predictive models capable of making accurate and reliable predictions of the modeled response of new compounds. MMDTA was a deep learning-based approach for predicting drug-target affinity using multimodal information from both drugs and targets. GNN and CNN were utilized to extract the sequence and structural features from the SMILES and 2D molecular graphs of drugs, respectively. As for its structural features, the distance matrix was first constructed based on the three-dimensional (3D) structure of target, followed by obtaining its structural features through a 2-dimensional convolutional neural network (2D-CNN).
Drug Discovery
Among the new targets are not only the classical receptors, but many enzymes that can be inhibited by binding the small molecule to them, as in the case of the BCL-2 inhibitor venetoclax currently on the market [55], or by hitting a regulator protein [56]. There are many examples in the history of pharmacy for drugs discovered by serendipity [14], starting with the most popular—the story about penicillin, a drug which saved millions of lives during the Second World War and for which Fleming, Florey and Chain received the Nobel Prize in 1945. In the 1930s, Leo Sternbach from the University in Cracow synthesized several heptoxdiazines in order to develop synthetic dyes. Cyclosporin was testing as an anti-tubercular antibiotic but became the first immunosuppressive drug that changed the science and practice of organ transplantation [15]. Additionally, the latest story is about sildenafil (Viagra), which was developing as an antihypertensive drug but is becoming one of the best-selling drugs ever, leading to an entirely new pharmacological group in modern pharmacology.
AI designs new drugs based on protein structures
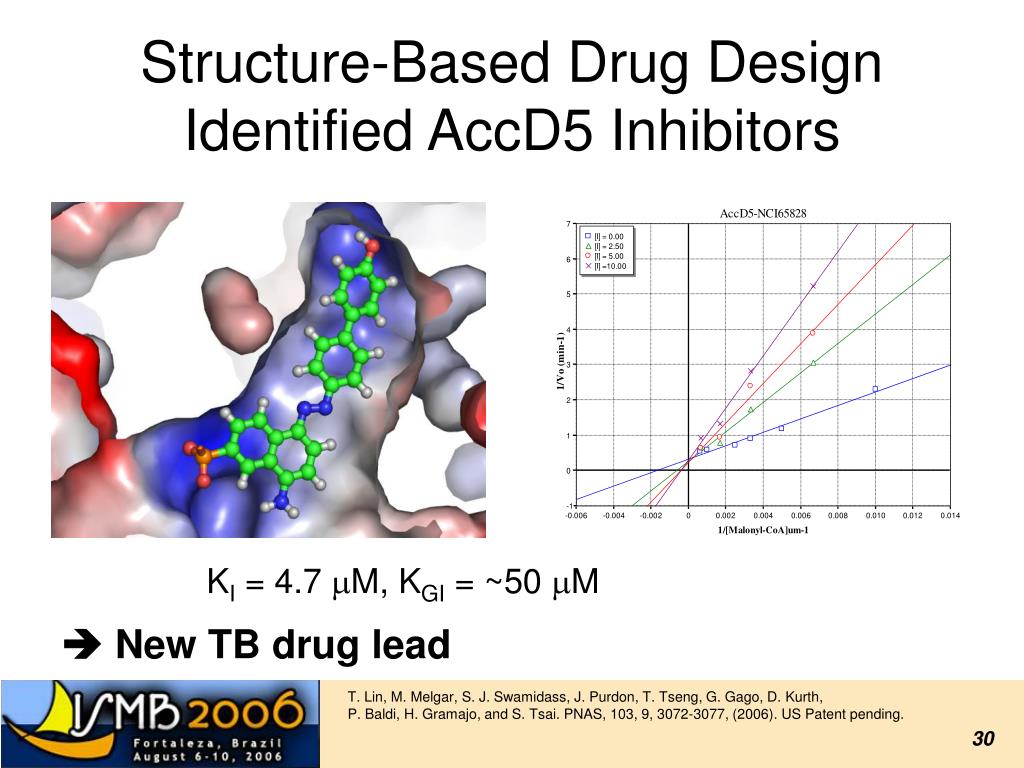
It is interesting to note that 221C7 contains a β-lactam ring, which may have activity beyond the scope of antibiotics. However, β-lactam ring compounds have potential side effects and risks relating to antibiotic resistance. The covalent warhead of β-lactam rings can bind irreversibly to target proteins, leading to side effects such as the generation of allergenic modified proteins49. In addition, the widespread use of β-lactams can increase the risk of antibiotic resistance, mainly due to the production of β-lactamase50. Examples A particular example of rational drug design involves the use of three-dimensional information about biomolecules obtained from such techniques as X-ray crystallography and NMR spectroscopy. Computer-aided drug design in particular becomes much more tractable when there is a high-resolution structure of a target protein bound to a potent ligand.
Rational Drug Design Process¶
A universal programmable Gaussian boson sampler for drug discovery - Nature.com
A universal programmable Gaussian boson sampler for drug discovery.
Posted: Thu, 12 Oct 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
To begin, drug SMILES was first processed into the molecular graphs using RDKit tool [39]. Subsequently, multi-scale graph neural network (MGNN) was employed to extract the structural features of drugs, and the extracted structural features were fused. With regards to the targets, multi-scale convolutional neural network (MCNN) was utilized to extract the sequence features from target sequences, and these features were fused as well. Next, the fused structural features of drugs and the fused sequence features of targets were concatenated to obtain the combined features of drug-target pair.
Many pretraining models based on long short-term memory (LSTM) or transformer architectures have been proposed, such as UniRep68 and TAPE69. To maintain the model consistency and gain parallel computing efficiency, we chose the transformer model in TAPE (TAPE-BERT) to calculate protein sequence embedding. The TAPE-BERT model contains 12 self-attention encoder layers, 12 attention heads for each layer, 768 dimensions for the hidden state, and 3072 dimensions for feedforward layers.
Psychedelic and Dissociative Drugs
There were several major achievements in the science of drug design that made it the main approach in the current and the future drug discovery [2]. In the early 1890s, Emil Fisher compared the drug–receptor interaction to the key and lock interplay. He considered that both the drug and the receptor interact as solid bodies without changing their conformations.
In parallel, information about the structural dynamics and electronic properties about ligands has also increased. Current methods for structure-based drug design can be divided roughly into two categories. The first category is about “finding” ligands for a given receptor, which is usually referred as database searching. In this case, a large number of potential ligand molecules are screened to find those fitting the binding pocket of the receptor.
The cells that produce collagen in livers are called hepatic stellate cells (HSC). In a new paper published in Cell Metabolism, scientists from the University of California San Diego investigated how these cells are activated. They found a three-component signaling pathway in the nucleus that functions according to a sort of police-controlling-the-police model. The synthesis and the full analytical characterization of the final compounds and intermediates are described in SI13. The pharmacokinetic profiles of compound 230D7 were determined in male BALB/c mice. The test compound 230D7 was dissolved in solution containing DMSO, PEG400, PBS (5/5/90, v/v) and administered via intraperitoneal administration (i.p.) at 10 mg/kg.
1) Random screening of synthetic compounds or chemicals and natural products by bioassay procedures. 2) Novel compounds preparation based on the known structures of biologically active, natural substances of plant and animal origin, i.e., lead skeleton. 3) Preparation of structural analogs of lead with increasing biological activity and 4) Application of bioisosteric principle. The PSCI PhD Program provides training that emphasizes basic as well as applied research through advanced coursework in contemporary pharmaceutical sciences.
Dr. Rogawski is Professor of Neurology and Pharmacology at the University of California, Davis School of Medicine. His research encompasses discovery of neurological therapeutics, characterization of drug mechanism, and early and later stage drug development. Dr. Rogawski is an elected fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science and was awarded the UC Davis Chancellor's Innovator of the Year Award for inventing the drug Zulresso™. Previously known as the Graduate Program in Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Sciences, the newly named Pharmaceutical Sciences and Drug Design in the School of Pharmacy at the University of Montana offers Master of Science and Doctoral degrees. The goal of the laboratory training received by the students is to design 'effective new drug therapies while minimizing adverse effects'.

No comments:
Post a Comment